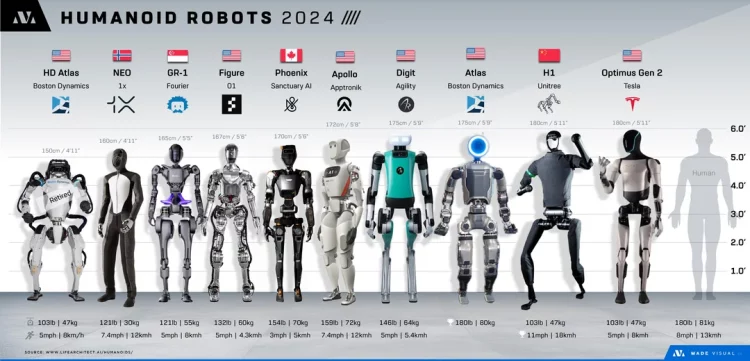
The humanoid robotics industry is rapidly evolving from experimental prototypes to commercially viable solutions capable of transforming manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, and commercial services. With advanced AI, improved actuators, and dexterous manipulation systems, humanoid robots are positioned to address complex tasks traditionally performed by humans. Market analysts now estimate a potential total addressable market (TAM) of $150 billion by 2035, reflecting a combination of technological feasibility, declining costs, and increasing adoption across multiple sectors. This analysis explores the parameters of the global TAM, the methodology used to forecast growth, adoption curves, regional differences, and the strategic implications for investors, governments, and enterprises.
Introduction: Defining the Parameters of the Global TAM
Total Addressable Market (TAM) represents the maximum revenue opportunity available if humanoid robotics were deployed to every feasible application worldwide. For the 2035 forecast, analysts considered four primary sectors:
- Manufacturing
- Humanoid robots can perform tasks ranging from assembly and quality control to complex dexterous operations in automotive, electronics, and consumer goods production.
- Robotics adoption in manufacturing is driven by labor cost efficiency, consistency, and productivity improvements.
- Logistics and Warehousing
- Robots capable of picking, packing, and moving goods reduce dependency on seasonal or manual labor.
- The integration of AI for navigation and object recognition enables autonomous warehouse operations at scale.
- Healthcare
- Humanoid robots assist with eldercare, patient monitoring, rehabilitation, and surgical support.
- As populations age, demand for scalable, reliable robotic assistance will increase significantly.
- Commercial and Service Sectors
- Robots in retail, hospitality, and customer service perform tasks such as reception, information assistance, and cleaning.
- Service-oriented applications enhance efficiency and reduce operational costs while improving user experience.
Defining the TAM requires not only identifying potential applications but also estimating robot density per application and the revenue generated per unit deployment over time.
Methodology: Bottom-Up Analysis
The TAM forecast relies on a bottom-up approach, aggregating potential revenue from each sector based on adoption potential, robot density, and cost per unit:
- Robot Density Estimation
- Analysts estimate the number of robots per facility or operational unit in each sector. For example, a mid-sized warehouse may deploy 50–200 robots depending on throughput requirements.
- Healthcare facilities are modeled with robots per bed or per care unit, considering both direct care and logistical support roles.
- Unit Economics and Pricing Models
- Initial costs for humanoid robots are high due to R&D and production scaling limitations, with prices ranging from $50,000 to $250,000 per unit.
- Over time, production efficiencies, standardization, and component cost reductions are expected to reduce unit prices, accelerating adoption.
- Revenue Aggregation
- Projected revenue is calculated by multiplying unit price by estimated deployment volume across sectors, adjusted for adoption curves and market penetration rates.
- Sensitivity analysis is applied to account for slower or faster-than-expected technological development, regulatory approval, and customer adoption behavior.
The bottom-up methodology provides a granular perspective on revenue potential, offering more actionable insights than top-down macroeconomic models alone.

Pricing and Adoption Curves: Costs Fall, Deployment Accelerates
Humanoid robot adoption will follow a classic S-curve, influenced by decreasing costs and increasing market familiarity:
- Early Adoption Phase (2025–2030)
- Initial deployments are concentrated in high-value applications such as advanced manufacturing and healthcare robotics.
- Unit costs remain high, limiting adoption to companies or institutions with significant capital budgets.
- Growth Phase (2030–2035)
- Standardization of components, AI improvements, and mass production reduce unit costs by 40–60%.
- Broader adoption occurs in logistics, commercial services, and mid-sized manufacturing facilities.
- Early adopters benefit from productivity gains, creating positive feedback loops that encourage wider deployment.
- Mature Phase (2035 and Beyond)
- Market penetration approaches saturation in high-volume sectors such as warehousing and eldercare.
- Competitive pressures further reduce costs, making humanoid robots accessible to small businesses and emerging markets.
The adoption curves suggest that market growth will be nonlinear, with rapid acceleration once cost thresholds align with economic feasibility across sectors.
Regional Breakdown: Which Markets Will Adopt Fastest
The TAM forecast also considers regional differences in labor costs, regulatory frameworks, and technological readiness:
- North America
- High-capital companies and technology-forward industries lead adoption.
- Manufacturing hubs, logistics networks, and healthcare facilities are early deployment areas.
- Europe
- Collaborative regulatory frameworks and social acceptance support service-oriented deployments.
- Healthcare and eldercare applications are projected to drive early adoption due to aging populations.
- Asia-Pacific
- China, Japan, and South Korea are at the forefront, driven by government incentives, strategic state-backed programs, and high population density.
- Manufacturing and logistics automation are key sectors, with a focus on high-volume industrial applications.
- Emerging Markets
- Adoption may lag due to capital constraints and regulatory hurdles.
- Service-oriented robots for retail and healthcare may accelerate adoption in urban centers.
Regional adoption rates impact the global TAM, as faster adoption in Asia-Pacific and North America significantly drives revenue projections.
Implications and Strategic Considerations
The $150 billion TAM by 2035 underscores both the scale and strategic importance of humanoid robotics. Stakeholders must consider several implications:
- Investment Strategy: Venture capital, corporate strategic investment, and government funding will play crucial roles in enabling market growth.
- Technology Prioritization: Companies developing advanced AI, actuators, and dexterous manipulation will capture the highest-value applications.
- Regulatory Planning: Regions with supportive yet responsible regulations will achieve faster adoption and stronger market growth.
- Global Competition: Market leaders will emerge from countries that balance technological innovation, cost-effective production, and ethical integration.
Call to Action
The humanoid robotics market represents a transformative opportunity with a potential $150 billion TAM by 2035. To explore the full 80-page report detailing sector-specific forecasts, pricing models, adoption scenarios, and regional projections, purchase our complete TAM forecast report. Detailed insights enable investors, corporate strategists, and policymakers to make informed decisions and capitalize on this emerging global industry.